The Era of Digital Manufacturing
The dawn of Industry 4.0 has brought with it a surge in digital manufacturing. With interconnected machines, advanced robotics, and AI-driven processes, the traditional shop floor is undergoing a digital metamorphosis. This paradigm shift is reshaping how industries function, driving efficiency and fostering innovation.
The Transformative Potential of Machine Data
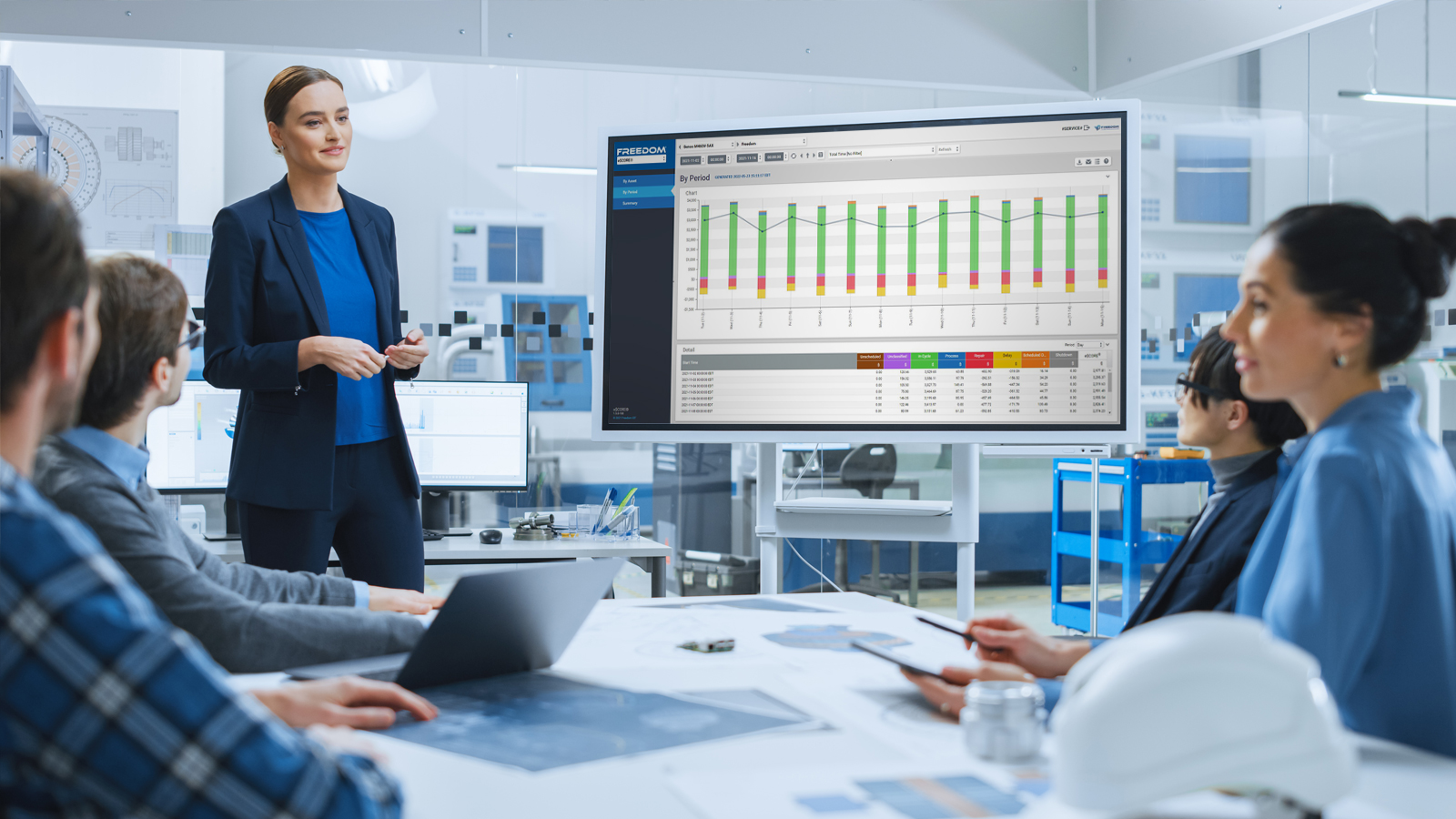
In this digital age, machine data has emerged as the linchpin of successful manufacturing operations. Acting as a constant digital stream of information, this data provides actionable insights that can drive process improvements, optimize operations, and reduce costs.
The Basics of Machine Data
What is Machine Data?
At its core, machine data represents the myriad of information generated by equipment during operations. This can range from temperature readings and machine runtimes to error codes and production counts. This continuous stream of data offers a real-time view of machine performance.
Common Sources of Machine Data on the Shop Floor
Different machinery populates the modern shop floor, from Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) to robotic arms. Each piece of equipment, aided by embedded sensors, produces vast amounts of data that reflect its current operational status.
The Importance of Understanding Machine Data

1. Improving Operational Efficiency
Machine data is a treasure trove for operational insights. By analyzing this data, manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, improve workflows, and ensure resources are used effectively, leading to cost savings and increased output.
2. Enhancing Product Quality
Consistent product quality is paramount. Through real-time monitoring, machine data can alert operators to variations, ensuring that products meet the established quality criteria, every time.
3. Predictive Maintenance and Reducing Downtime
By analyzing patterns and trends in machine data, it’s possible to predict when equipment might fail. This allows for timely maintenance, reducing costly unplanned downtimes.
Tools and Technologies for Capturing Machine Data

1. Sensors and IoT Devices
Advanced sensors, from thermocouples to accelerometers, gather specific machine metrics. When paired with IoT devices, this data is sent in real-time for centralized analysis, forming the backbone of smart manufacturing.
2. Data Acquisition Systems
Data acquisition systems play a pivotal role in consolidating data from myriad sources, ensuring that it’s structured, synchronized, and ready for evaluation.
3. Edge Computing on the Shop Floor
Edge computing processes data close to its source. This reduces latency, enabling faster decision-making, and ensuring that only relevant data is sent to centralized systems, reducing data transfer loads.
Navigating Shop Floor Layout with Machine Data

1. Mapping Machine Locations and Functions
Using machine data, manufacturers can derive optimal layouts. Proper placement can reduce transfer times between machines, leading to smoother workflows.
2. Using Machine Data for Optimal Workflow Design
Real-time data can unveil inefficiencies in workflows. With this insight, processes can be redesigned for maximum efficiency and output.
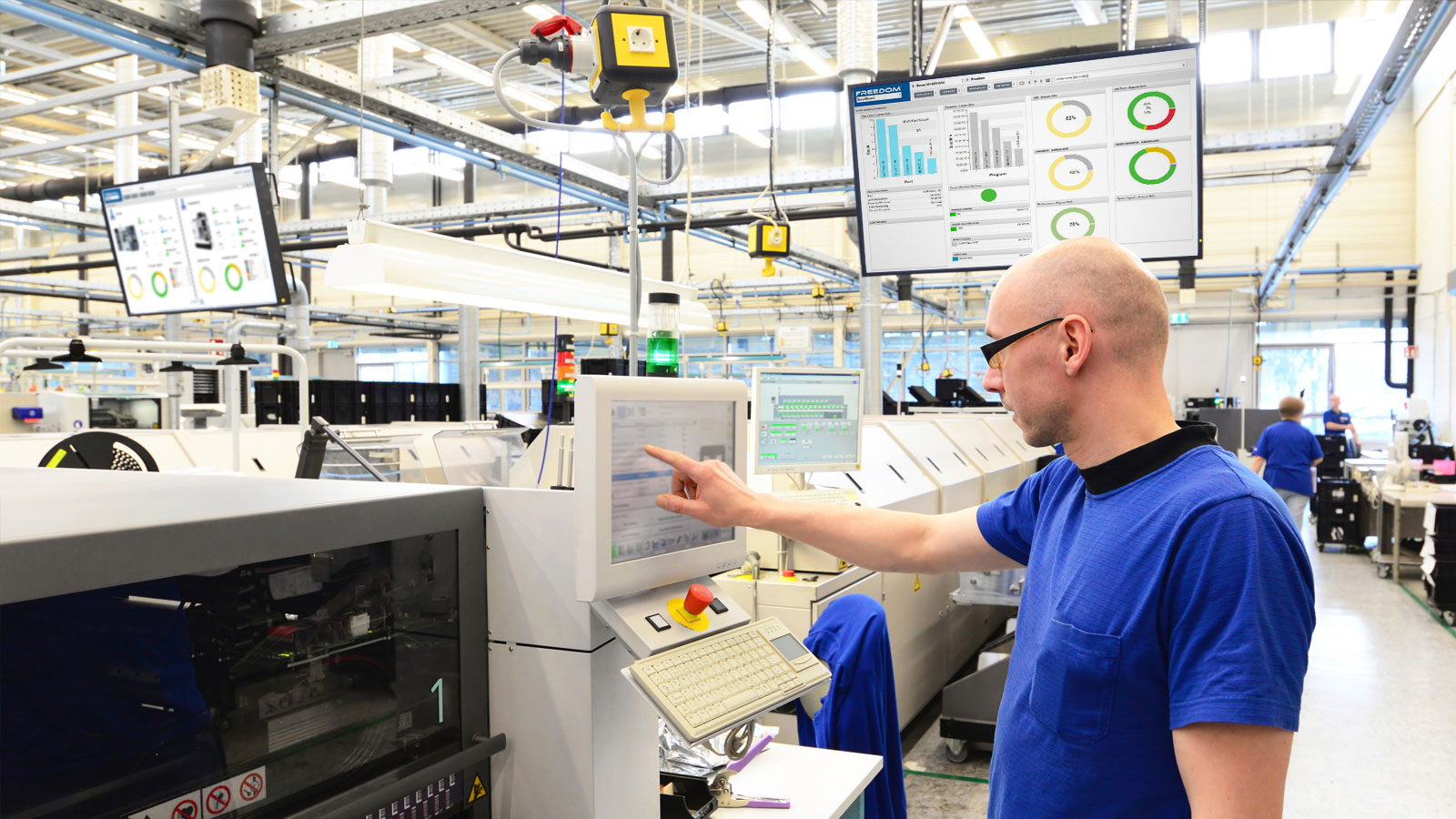
3. Real-time Tracking and Analysis for On-the-spot Decisions
Immediate access to machine data enables managers to make rapid decisions, from adjusting machine settings to reallocating resources, all in real-time.
Harnessing Machine Data for Quality Control
1. Monitoring Production Parameters
Keeping a constant eye on production parameters like temperature, pressure, or speed ensures each product is made consistently and meets quality standards.
2. Spotting Anomalies in Real-time
By setting thresholds on specific metrics, anomalies can be instantly identified, triggering immediate interventions and reducing defective products.
3. Refining Processes Based on Data Feedback
Continuous feedback loops, powered by machine data, allow manufacturers to fine-tune their processes, enhancing quality and efficiency.
Optimizing Machine Performance with Data

1. Data-driven Machine Calibration
Instead of routine calibrations, data-driven calibrations ensure machines are adjusted only when necessary, guaranteeing optimal performance.
2. Predictive Analytics for Wear and Tear
Machine wear is inevitable. However, by analyzing machine data, it’s possible to predict when wear might affect performance, allowing for preemptive maintenance.
3. Energy Consumption Optimization
By monitoring energy usage patterns, manufacturers can run machines during off-peak hours or adjust processes to minimize energy consumption, leading to cost savings.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Machine Data Strategies
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
As with all digital data, machine data is susceptible to breaches. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect this sensitive information.
Integrating Legacy Systems with Modern Data Tools
Not all machines on the shop floor are modern. Integrating older, legacy systems with newer data tools can be challenging but is essential for holistic insights.
Addressing the Skills Gap in the Workforce
The digital transformation brings a skills gap. Investments in training and upskilling are critical to ensure the workforce can thrive in a data-driven environment.
Closing Thoughts
From mere operational logs to a transformational tool, machine data revolutionizes manufacturing, drives efficiency, and fosters innovation.
Key Takeaways and Best Practices for Businesses
Harnessing machine data is not just about technology but also about strategy. Prioritizing data security, continuous training, and adaptability are crucial for success.